The coronavirus outbreak has struck a significant blow to the Chinese economy. The severity of this hit will not only depend on the extent and depth of the outbreak, but also on the government's response. Here is why China should avoid coal power investments when stimulating the economy after COVID-19 has been contained.
The Embodied Carbon Conundrum: Solving for All Emission Sources from the Built Environment
Increasing urgency among policymakers and the design community to meet the goals of the Paris Climate Accord has spurred more aggressive codes and energy policies in jurisdictions around the United States. These strategies are making gains on driving down carbon emissions resulting from powering our homes and commercial buildings. Yet another source of carbon — embodied carbon — has gone largely unaddressed.
U.S. Coal Fired Power Plants Closing Fast
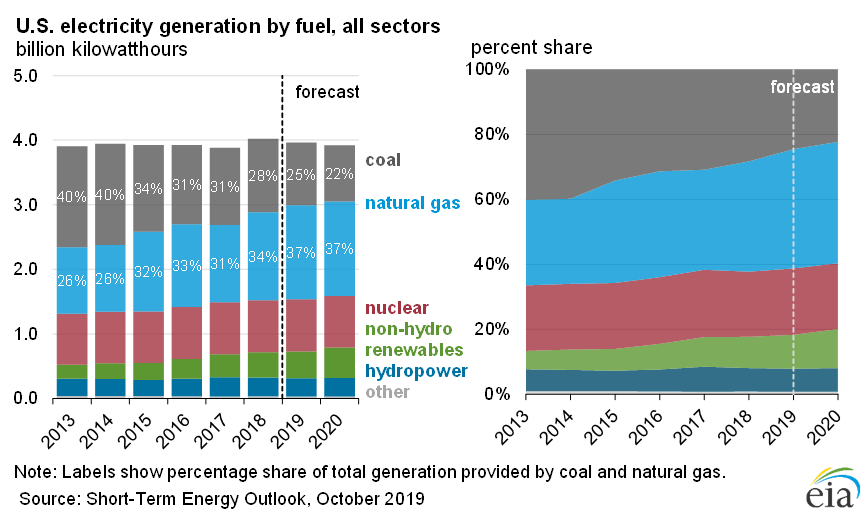
EIA Forecasts Diminishing Share of Energy Generation From Coal By 2020
The EIA forecasts that the share of U.S. generation from coal will average 25% in 2019 and 22% in 2020, down from 28% in 2018.
See the full forecast here.
Interactive Map Shows Changes in Global Coal Power Since 2000
The organization Carbon Brief has built an interactive website where you can explore the capacity changes in coal power since the year 2000.
See the interactive website here.